Learn Mix design of M25 Grade Concrete as per Indian standard codebooks – IS10262 -CONCRETE MIX PROPORTIONING – GUIDELINES and IS456.
I. STIPULATIONS FOR PROPORTIONING
This section contains the conditions or requirements specified or expected from the concrete. you can adjust the values in the section to suit your needs
Please view on Landscape mode to get better view on a mobile phone.
| A | Grade Designation | M25 | |
| B | Type of Cement | OPC 53 | |
| C | Maximum Nominal Size of Aggregate | 20mm | |
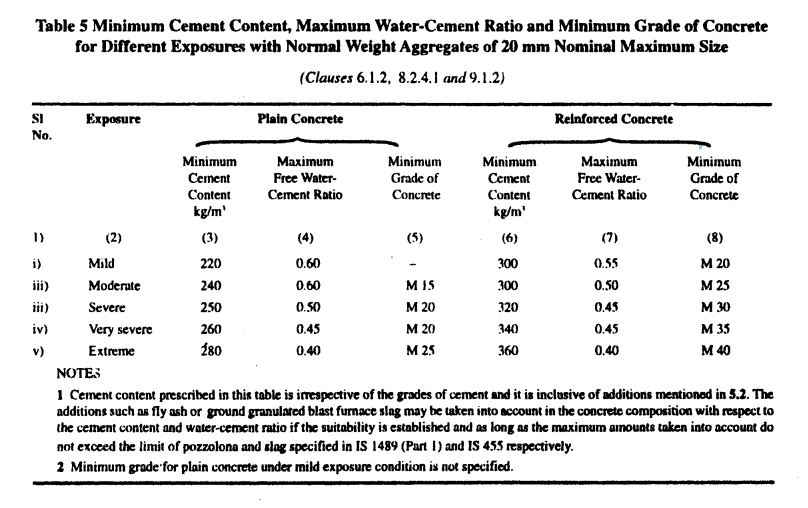
| D | Minimum Cement Content | 300kg | Table 5-IS456 |
| E | Maximum Cement Content | 450kg | As per clause 8.2.4.2 |
| F | Maximum W/C ratio | 0.50 | Table 5-IS456 |
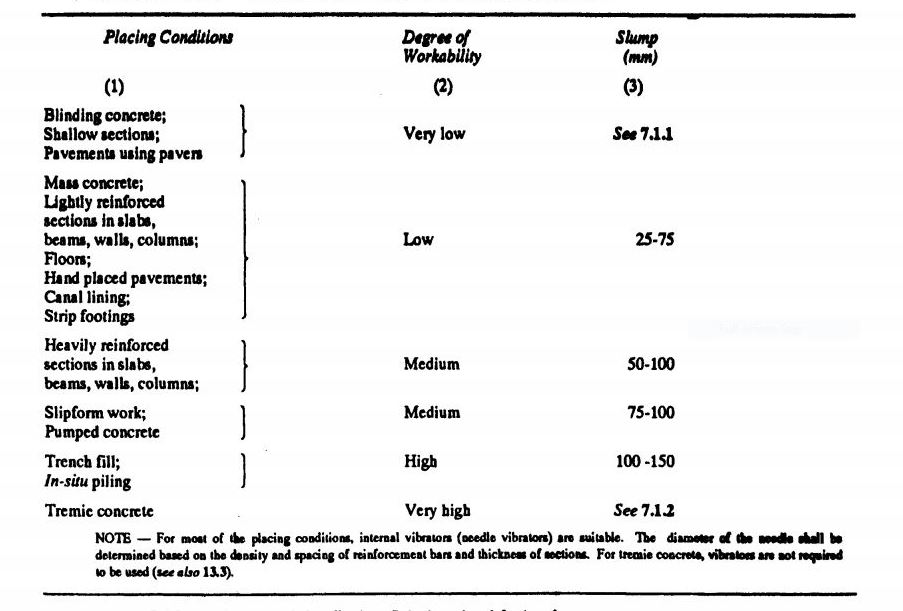
| G | Workability | 75mm | For RCC As per code |
II. TEST DATA FOR MATERIALS
The values in this section should be based on laboratory tests on materials according to the relevant code book. The values given here are the standard values of everyday construction materials used in India.
| A | Cement Used | OPC 53 | Confirming to IS8112 |
| B | Specific Gravity of Cement | 3.15 | Test – IS: 2720 |
| C | Specific Gravity of | Test – IS 2386 | |
| Coarse Aggregate | 2.74 | ||
| Fine Aggregate | 2.74 | ||
| D | Water Absorption | Test – IS 2386 | |
| Coarse aggregate | 0.5 % | ||
| Fine aggregate | 1 % | ||
| E | Sieve Analysis | Test – IS 2386 | |
| Coarse aggregate | Confirming to Table 2-IS383 | ||
| Fine aggregate | Zone II | Confirming to Table 4-IS383 |
III. TARGET STRENGTH
The mixing method, climate, curing and other factors can affect the strength of the concrete, so it is important to design the concrete with greater strength than the actual requirement.
Target strength (Fck) must be greater than the Designated Characteristic strength (fck). The target strength for m20 grade concrete can be found from the formula given in the code book.
Fck = = fck.+1.65s
Standard deviation (S) value for the M25 grade concrete is given in table 1 of IS10262.
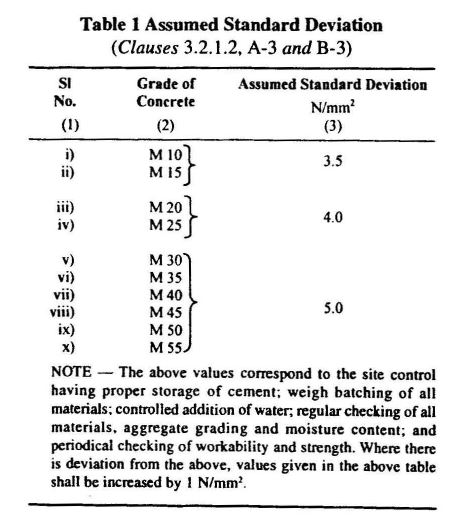
| Fck | = fck.+1.65s | “S” from Table1-IS10262 |
| Fck | = 25+(1.65 x 4) | S = 4 |
| Fck | = 31.6 N/mm2 |
The target strength required for our concrete is 31.6 N / mm2. That is, after curing in water for 28 days, the compressive strength of the concrete should be at least 31.6 N / mm2 when tested on a direct compression test machine (CTM).
IV. SELECTION OF WATER-CEMENT RATIO
The maximum water-cement ratio for M25 grade concrete can be found in Table 5-IS456 given above.
| Maximum W/C ratio | =0.50 | Table 5-IS456 |
| Adopted W/C ratio | =0.50 |
You can reduce the water-cement ratio for M25 grade concrete based on your requirements, but remember that the Water-cement ratio directly affects the strength of the concrete.
V. SELECTION OF WATER CONTENT
Maximum water content to get slump up to 50mm when using a 20mm aggregate is used is given in Table 2 of IS10262.
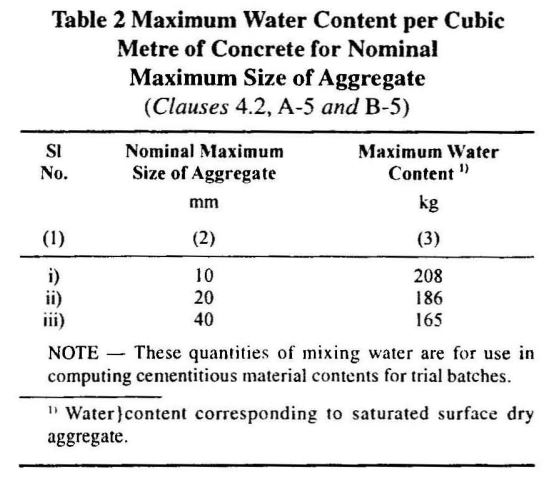
If we use 20mm aggregate we need the following water content to get a 50mm slump in concrete
| Maximum Water Content | = 186 L |
However, according to the specification given in Section 1, our concrete requires a slump of 75 mm. Clause 4.2 of IS Code suggest an increase of 3% in water content would result in increase in slump of 25 mm from the actual 50 mm slope.
Therefore, to obtain a slump of 75 mm over a total of 20 mm:-
| Water-content for 75mm Slump | = 186+(0.03*186) | As per Clause 4.2 |
| = 191.58 L | ||
| Adopted Water Content | = 190 L |
VI. CALCULATION OF CEMENT
The weight of cement required for M25 grade concrete can be calculated from the water-cement ratio and the water content.
| Adopted Water Cement Ratio | = 0.50 |
| Cement required | = Water Content / W-C Ratio |
| = 190/0.5 | |
| = 380 kg | |
| Adopted Cement Content | = 380 kg |
VII COARSE AND FINE AGGREGATE
The coarse aggregate ratios for different zones of fine aggregates are given in Table 3 of IS10262.
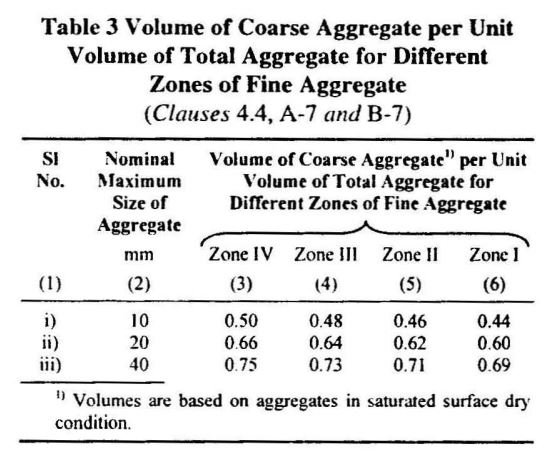
As per specification, for Maximum Nominal size of aggregate = 20mm & Fine aggregate = Zone II:-
| Coarse Aggregate ratio | =0.62 | Table3-IS10262 |
| Final Fine Aggregate ratio | = 0.38 | (1-0.62) = 0.38 |
VIII MIX CALCULATIONS OF M25 GRADE CONCRETE
This section deals with calculation of fine aggregate and coarse aggregate from aggregate ratios, cement and water.
| A | Volume of Concrete | = 1 cu.m |
| B | Total Volume of Cement | = Cement/(S.G*1000) |
| = 380/(3.15*1000) | ||
| = 0.121 cu.m | ||
| C | Volume of Water | = Water /(S.G*1000) |
| = 190/(1*1000) | ||
| = 0.190 cu.m | ||
| D | Total Aggregates requirement | = A – (B+C+D+E) |
| = 1 -(0.121+0.190) | ||
| = 0.689 cu.m | ||
| E | Coarse Aggregate (C.A) | = F * C.A ratio * S.G * 1000 |
| = 0.689*0.62*2.74 *1000 | ||
| = 1171 kg | ||
| F | Fine Aggregate (F.A) | = F * F.A ratio * S.G * 1000 |
| = 0.689*0.38*2.74 *1000 | ||
| = 717 kg |
Cement Fine and Coarse Aggregate needed for M25 grade concrete
| S.No. | MATERIALS | QUANTITY |
| 1 | Cement | 380 kg |
| 2 | Fine Aggregate | 717 kg |
| 3 | Coarse Aggregate (20mm) | 1170 kg |
| 4 | WATER | 190 L |
To find the design mix ratio, divide the calculated value of all materials by the weight of the cement. Therefore the Mix Design Ratio of M25 Grade concrete by weight is Cement: F.A: C.A: Water = 1: 1.9 :3.1 : 0.50
Note: This is a Design mix ratio by weight which is different from the Nominal volumetric mix ratio. Read this post to understand the difference between Nominal Mix and Design Mix.

Leave a Reply