This article covers the Mix design of M20 Grade Concrete as per the Indian standard codebook – CONCRETE MIX PROPORTIONING – GUIDELINES – IS10262 & IS456.
I. STIPULATIONS FOR PROPORTIONING
This section deals with the conditions or requirements expected from concrete. To design m20 quality concrete mix, adjust the values in this section to suit your needs.
For a better view of mobile phones, see Landscape Mode.
| A | Grade Designation | M20 | |
| B | Type of Cement | OPC 53 | |
| C | Maximum Nominal Size of Aggregate | 20mm | |
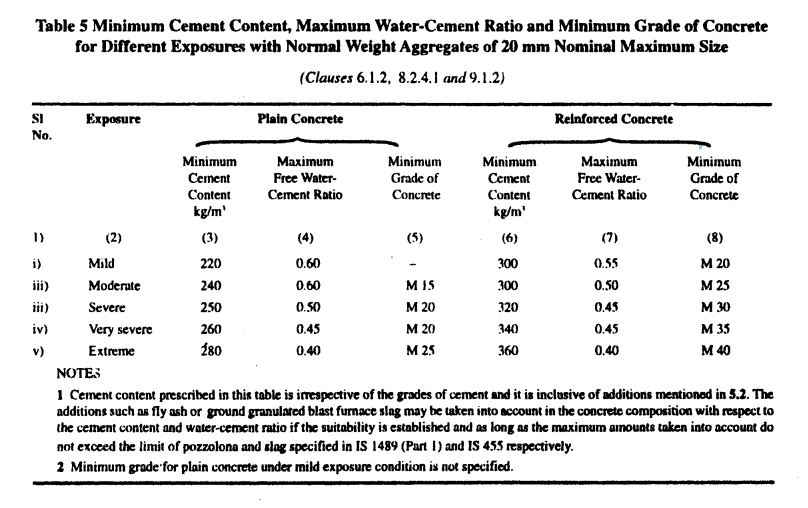
| D | Minimum Cement Content | 300kg | Table 5-IS456 |
| E | Maximum Cement Content | 450kg | As per clause 8.2.4.2 |
| F | Maximum W/C ratio | 0.55 | Table 5-IS456 |
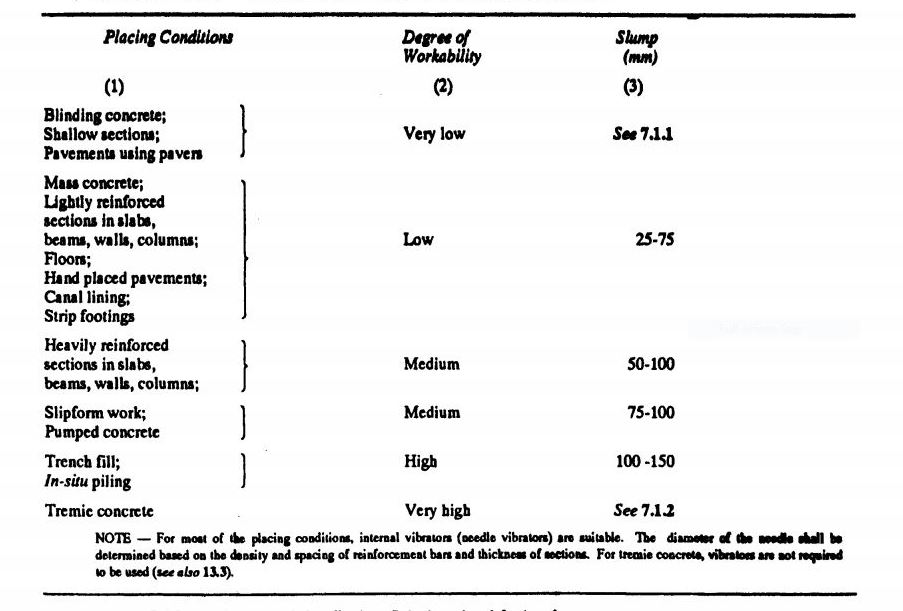
| G | Workability | 75mm | For RCC As per code |
II. TEST DATA FOR MATERIALS
The values in this section should be based on laboratory tests. Here, standard values of different materials are considered for the Mix design of M20 grade concrete.
| A | Cement Used | OPC 53 | Confirming to IS8112 |
| B | Specific Gravity of Cement | 3.15 | Test – IS: 2720 |
| C | Specific Gravity of | Test – IS 2386 | |
| Coarse Aggregate | 2.74 | ||
| Fine Aggregate | 2.74 | ||
| D | Water Absorption | Test – IS 2386 | |
| Coarse aggregate | 0.5 % | ||
| Fine aggregate | 1 % | ||
| E | Sieve Analysis | Test – IS 2386 | |
| Coarse aggregate | Confirming to Table 2-IS383 | ||
| Fine aggregate | Zone II | Confirming to Table 4-IS383 |
III. TARGET STRENGTH
In addition to the composition of the mixture, the strength of the concrete depends on other factors, such as environmental temperature, mixing method, curing etc. Therefore the Target strength (Fck) of the concrete should be higher than the Characteristic strength (fck) for protection.
The Target strength for m20 grade concrete can be found from the formula given in the code book.
Fck = = fck.+1.65s
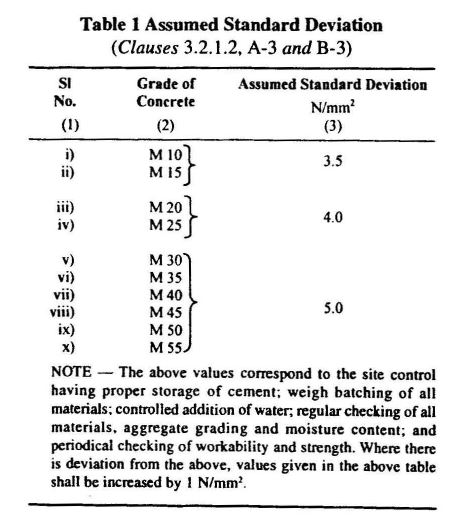
The Standard Deviation (S) value for M20 grade concrete is given in Table 1 of IS10262.
| Fck | = fck.+1.65s | “S” from Table1-IS10262 |
| Fck | = 20+(1.65 x 4) | S = 4 |
| Fck | = 26.6 N/mm2 |
After 28 days of curing, the concrete should have a compressive strength greater than 26.6 N / mm2. This can be confirmed by a compression test on Compression Testing Machine (CTM).
IV. SELECTION OF WATER-CEMENT RATIO
The maximum Water-Cement ratio for M20 grade concrete can be found inTable 5-IS456 which is given below.
| Maximum W/C ratio | =0.55 | Table 5-IS456 |
| Adopted W/C ratio | =0.55 |
You can adjust the Water-Cement ratio based on your requirements but keep in mind that the Water-Cement ratio directly affects the strength of the concrete.
V. SELECTION OF WATER CONTENT
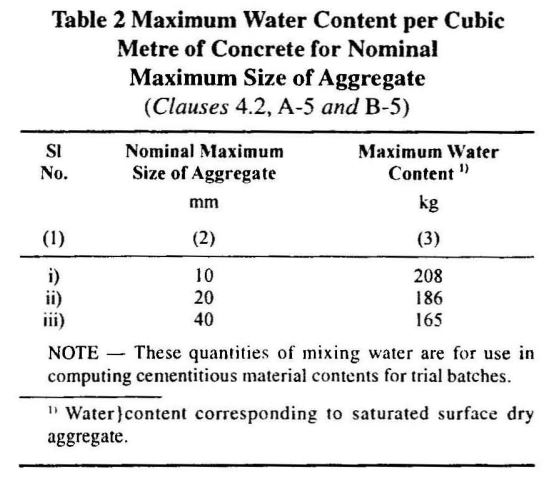
The Maximum Water Content required to obtain a slump of 50 mm in concrete is given in Table 2 of IS10262.
For 20mm aggregate and 50mm slump :-
| Maximum Water Content | = 186 L |
But our concrete requires a slope of 75mm as per the specification given in Section 1.
Section 4.2 recommends increasing the water content by 3% to obtain extra 25 mm slump in concrete
For aggregate = 20mm and Slump = 75mm
| Water-content for 75mm Slump | = 186+(0.03*186) | As per Clause 4.2 |
| = 191.58 L | ||
| Adopted Water Content | = 190 L |
VI. CALCULATION OF CEMENT
The weight of cement required can be calculated from the Water-Cement ratio and the Water content.
| Adopted Water-Cement Ratio | = 0.55 |
| Cement required | = Water Content / W-C Ratio |
| = 190/0.55 | |
| = 345.45 kg | |
| Adopted Cement Content | = 345 kg |
VII COARSE AND FINE AGGREGATE
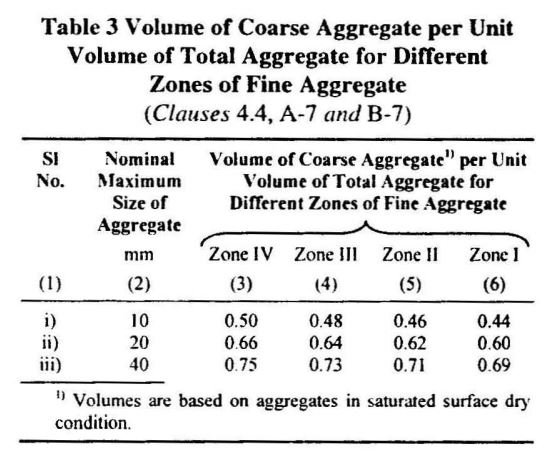
Table 3 of IS10262 gives Volume of coarse aggregate ratios per unit volume of Total Aggregate for different zones of fine aggregates. These ratios are valid for 0.5 water-cement ratio.
For aggregate = 20mm, Fine aggregate= Zone II, Water-cement ratio = 0.50
| Coarse Aggregate ratio (For W/C =0.5) | =0.62 | Table3-IS10262 |
But our water- cement ratio is 0.50. To increase water-cement ratio by 0.05, the C.A ratio should be reduced to 0.01 and vice versa. So subtract 0.01 from the C.A ratio above.
For aggregate = 20mm, Fine aggregate= Zone II, Water-cement ratio = 0.55
| Coarse Aggregate ratio (For W/C =0.5) | =0.62 | Table3-IS10262 |
| Coarse Aggregate ratio (For W/C =0.55) | =0.61 | (0.62-0.01 = 0.61) |
| Final Fine Aggregate ratio | = 0.39 | (1-0.61) = 0.39 |
VIII MIX CALCULATIONS OF M20 GRADE CONCRETE
Here we are going to look at how to calculate fine aggregate and coarse aggregate from aggregate ratio, cement content and water content.
| A | Volume of Concrete | = 1 cu.m |
| B | Total Volume of Cement | = Cement/(S.G*1000) |
| = 345/(3.15*1000) | ||
| = 0.110 cu.m | ||
| C | Volume of Water | = Water /(S.G*1000) |
| = 190/(1*1000) | ||
| = 0.190 cu.m | ||
| D | Total Aggregates requirement | = A – (B+C+D+E) |
| = 1 – (0.110+0.190) | ||
| = 0.7 cu.m | ||
| E | Coarse Aggregate (C.A) | = F * C.A ratio * S.G * 1000 |
| = 0.7*0.61*2.74 *1000 | ||
| = 1170 kg | ||
| F | Fine Aggregate (F.A) | = F * F.A ratio * S.G * 1000 |
| = 0.7*0.39*2.74 *1000 | ||
| = 748 kg |
Cement, Fine and Coarse Aggregate needed for M20 grade concrete
Therefore, to produce one cubic meter of m20 grade concrete, we need the following quantities of cement, fine aggregate (sand), coarse aggregate (stone) and water.
| S.No. | MATERIALS | QUANTITY |
| 1 | Cement | 345 kg |
| 2 | Fine Aggregate | 750 kg |
| 3 | Coarse Aggregate (20mm) | 1170 kg |
| 4 | WATER | 190 L |
Too find the design mix ratio, divide the calculated value of all materials by the weight of the cement. Therefore the Mix ratio of M20 grade concrete is Cement: F.A: C.A: water = 1: 2.17: 3.4: 0.55
Note: This is a Design mix ratio which is different from the Nominal volumetric mix ratio. Read this post to understand the difference between Nominal Mix and Design Mix.
Leave a Reply